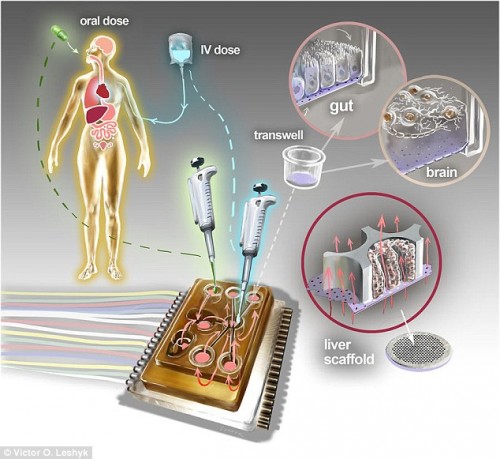
MIT scientists have built a radical device that may revolutionize the way we conduct drug testing in the future.
The paperback-sized device, called a 'body-on-a-chip,' can hold up to 10 artificial 'human' organs.
Similarly, researchers have created an 'organ-on-a-chip,' 'menstrual-cycle-on-a-chip' and a 'stem-cell-on-a-chip.'
But
unlike those devices, MIT's microfluidic device is able to simulate how
a drug might effect several key organs, rather than, say, just the
liver.
Microfluidic platforms place various kinds of human cells into a device and then push fluid through them to model blood flow, according to MIT.
They're made of a block of plastic that includes compartments to accommodate a 'microphysiological system' (MPS), with various compartments that let fluids pass through, so as to mimic a circulatory system.
The
device also has a water reservoir that limits evaporation and maintains
humidity, as well as a water pump that's built into the underside of
the platform.
This latest version can combine cells from 10 different organs, including the liver, lung, gut, endometrium, brain, heart, pancreas, kidney, skin and skeletal muscle.
Scientists are able to precisely control the flow of molecular exchanges, as well as drug distribution.
The 'body-on-a-chip' is also reusable and in the MIT study, organs were stable for up to four weeks.
In the future, it might allow scientists to no longer rely on animals like mice for early-stage drug testing.
Additionally,
testing drugs on model organs can also provide a more accurate reading
on how a real human body would react to drugs, since animal organs tend
to vary in size and composition compared to ours.
Before this device, no one had successfully connected more than a few different tissue types on one platform, MIT noted.
Additionally, most platforms are a closed system, making it hard to manipulate what was happening inside the chip.
Instead,
the body-on-a-chip is an open system, which removes the lid and makes
it easier to manipulate the platform and remove samples for analysis,
MIT said.